No one is immune to tricksters, so the better you can spot a scam email, the safer your inbox remains. This guide helps you distinguish between phishing and spoofing, spot red flags, and know what action to take.

What Are Scam Emails?
Scam emails are fraudulent messages that aim to deceive you either by impersonating others (spoofing) or by tricking you into acting (phishing).
- Spoofing is when the sender’s identity is forged, making the mail appear to come from someone trusted (for instance, your bank or 1-grid).
- Phishing is when the scam tries to lure you into revealing sensitive information (passwords, credit cards) or clicking on malicious links, all under false pretences.
IMPORTANT: Although phishing often uses spoofing techniques, not all spoofed emails are phishing attacks, so it is important to know how to spot a scam email and which type it is.
Phishing vs Spoofing: What Sets Them Apart
| Feature | Phishing | Spoofing |
| Goal | Trick you into disclosing data or credentials | Malicious link, form, or login page |
| Typical action | Content and recipient behaviour | Sanctioned email header impersonation |
| Relationship | Uses social engineering | Focuses on encryption and sender identity forgeries |
| Detection filter | Content and recipient behaviour | Impersonate the sender to bypass trust |
Key Red Flags to Watch Out For
- Mismatched sender display name vs email address.
- Urgent or scare tactics (“Your account will be closed”).
- Unexpected attachments or file types you don’t trust.
- Links that don’t match the sender’s domain.
- Poor grammar, odd formatting, odd greetings.
- Requests for passwords or personal data via email.
- Emails from known contacts but with strange content.
How to Inspect an Email
It’s important to understand if it is a spoofing or phishing attack, and what to look out for in the scam email to protect yourself. Here’s a list of things on how to spot a scam email.
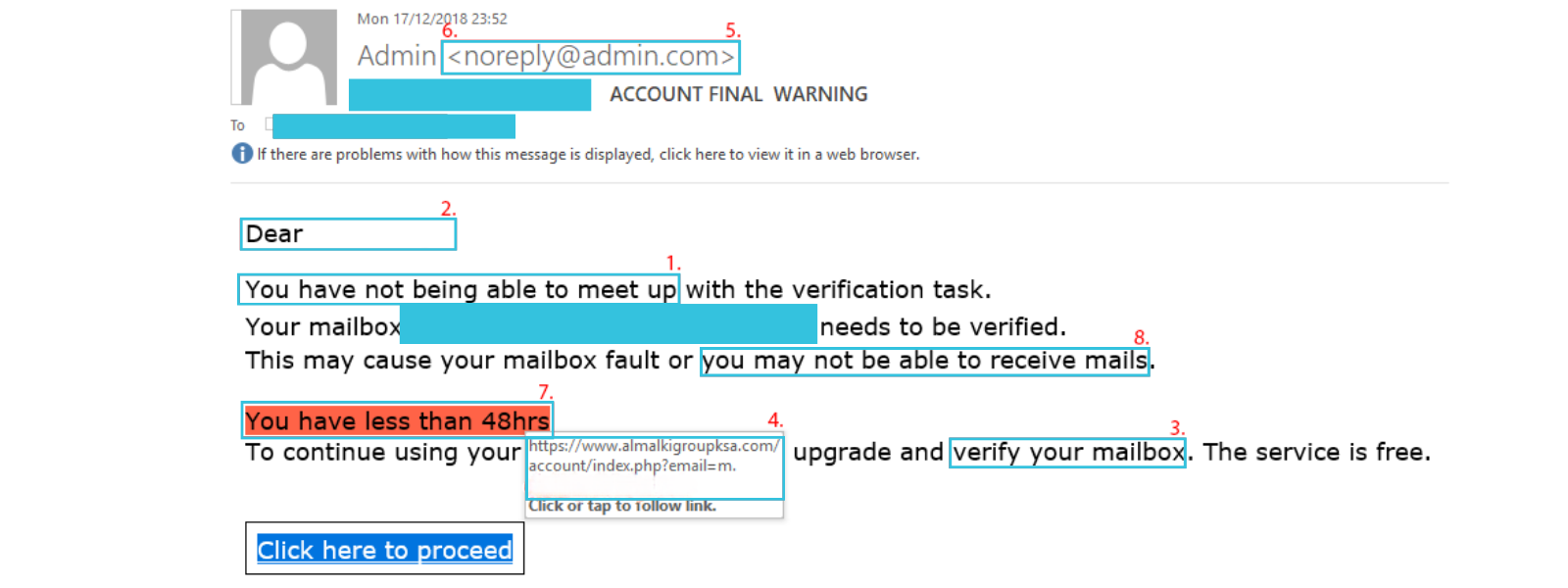
1. The email contains poor spelling and/or grammar.
Phishing emails may contain poor spelling and grammar. Also look out for inconsistencies in the presentation of the email (e.g. the email may contain various font styles, font sizes and mismatched branding).
2. The email contains an impersonal greeting.
Phishing emails will often contain greetings such as “Hi”, “Hi <email address>”, or “Dear Customer”.
3. The email asks for your personal information.
Nobody at a company will ask for your sensitive information (e.g. personally identifiable data, usernames and passwords, or banking information) by email or by phone.
4. The email contains a mismatched URL.
Phishing emails often contain embedded links disguised as legitimate websites. Those embedded links probably won’t direct you where you’d expect them to. If it looks suspicious, hover your mouse over the top of the link to check if the hyperlinked address matches the one in the email.
5. The email contains a misleading domain (e.g. 1grid.com) name.
Malicious actors often attempt to ‘spoof’ legitimate domain names to give the impression that embedded links will direct to legitimate websites. For example, 1-grid.com is a legitimate email, whereas 1grid.com is not.
6. The email contains an unusual ‘from’ address.
Malicious actors often attempt to ‘spoof’ legitimate email addresses to give the impression that the email is being sent from a legitimate organisation or person, while it is a scam email.
What does this tactic hide?
This tactic often hides unusual email addresses behind what appears to be a genuine sender name. If the email looks suspicious, hover your mouse over the sender’s name to see the email address from which the email was sent.
7. The email creates a sense of urgency.
Phishing emails may attempt to create urgency by warning you that your 1-grid domain may expire or that your account has been suspended to encourage you to take immediate action.
8. The email contains unrealistic threats.
Similarly, phishing emails may also attempt to create urgency by using intimidation to scare victims into disclosing sensitive information or making a payment.
What to Do When You Spot a Scam
- Do not click any links or download attachments.
- Next, mark the email as spam or phishing in your email client.
- Then, forward the suspicious email (with full headers) to 1-grid Support for review (if it is an impersonation of 1-grid) or to your IT team.
- If you entered any credentials, change them immediately and then enable two-factor authentication.
- Warn others in your team or network if applicable.
Prevention Tips and Best Practices
- Use authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) so spoofed emails are more likely to be blocked (see How to Prevent Email Spoofing Attacks).
- Keep your DNS records clean and up to date.
- Use reputable antivirus and anti-phishing tools.
- Educate yourself and your team about scam types.
- Regularly monitor email logs or DMARC reports for anomalies.
FAQs
I got an email that looks exactly like one from 1-grid. How do I know if it’s fake?
Check the sender’s actual email, inspect full headers, then verify SPF/DKIM results, and look for subtle red flags like typos or unusual requests. It’s important to know how to spot a scam email before taking any action on it.
Official emails will always only come from “1-grid.com”, but if you are ever unsure, please reach out to our Support Team for clarity.
Can I trust a link if the display text looks normal?
Not always. Always hover or inspect link targets. Attackers can display normal text but link to malicious sites.
What if the spoofed email is just spam and not phishing?
Even spam with spoofed identities is dangerous, as it may lead to phishing later. Treat spoofed emails with caution.
Does marking as spam protect me fully?
It helps train your email provider’s filters, but it doesn’t fix domain-level issues. Always use authentication and best practices.
How often should I review DNS and email authentication settings?
At least annually, or whenever you add new services, domains, or email providers.
Additional Resources
How to Prevent Email Spoofing Attacks
What Is Email Spoofing? How It Works and How to Protect Yourself
Email Headers FAQs
How to Enable DKIM and SPF on Your Mail Domain
Why SSL? The Purpose of Using SSL Certificates
Settings to Configure Your 1-grid Email Accounts Across Devices
What is a Domain Name Server (DNS)?
MailChannels FAQs
SpamTitan FAQs
Need Additional Support?
We’re Here to Help:
Receiving and handling a spoofing or phishing scam email doesn’t have to be scary with this easy-to-reference guide. Stuck? Contact our Support Team for guidance (https://1grid.co.za/contact-us/). We’re ready to see how we can help!
